What is Dysgraphia?
Dysgraphia is a neurological disorder of written expression that impairs writing ability and fine motor skills. It is a learning disability that affects children and adults and interferes with practically all aspects of the writing process, including spelling, legibility, word spacing and sizing, and expression.
It’s estimated that 5 to 20 percent of all children have some type of writing deficit like dysgraphia.1 Dysgraphia and other learning disorders, like dyslexia and dyscalculia, are common in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD or ADD); Up to half of children with ADHD in the U.S. have a learning disorder.2
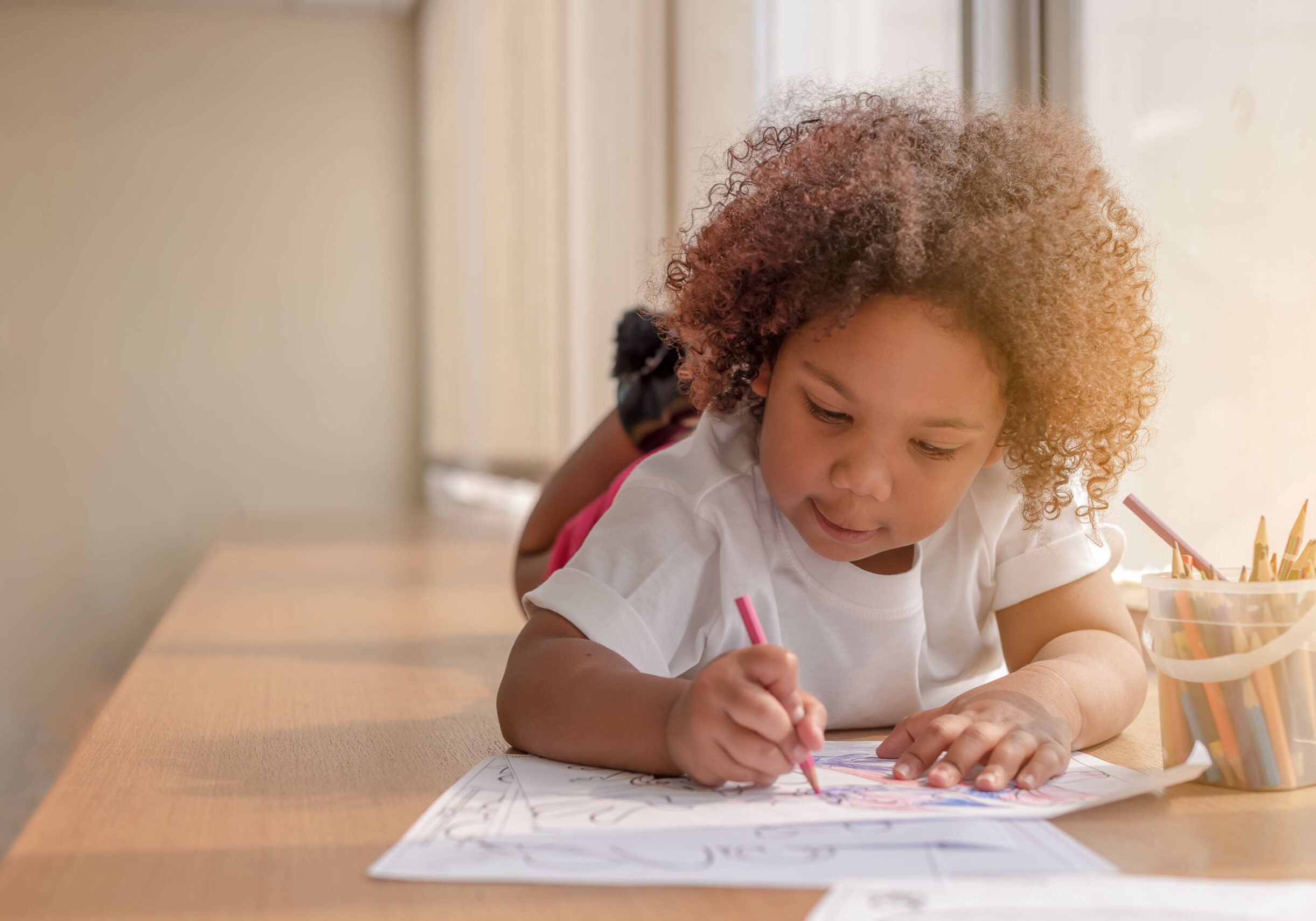

Dysgraphia Signs
-
-
Messy handwriting
-
Poor legibility
-
Unfinished letters.
-
Letter reversal, inversion, transpositions and elision
-
Slow writing speed
-
Irregular letter size
-
Letters may not sit on the line
-
Mix of cursive and non-cursive styles
-
Letters are bunched or spaced unevenly
-
Writing isn’t justified to left of page
-
Odd posture, pencil grip or paper angle
-
Writing fatigue and crampingMay have difficulty with other fine motor skills such as tying shoelaces
-
May have difficulty with other fine motor skills such as tying shoelaces
-
Slow copying speed.
-
Need to watch pen to write legibly.
-
Inconsistent letter formation
-
Slow or labored writing (which may be neat) literacy skills / orthographic coding and processing
-
Poor spelling
-
May skip words
-
Poor punctuation
-
Word errors - writing a different word than the target
-
Difficulty with syntax structure or grammar
-
Words ordered incorrectly
-
Incorrect verb and pronoun usage
-
Difficulty putting ideas in writing
-
Writing that lacks coherence
-